Symptoms & Causes
Ankylosing Spondylitis is an autoimmune inflammatory disease. The immune system attacks the joints of the spine & pelvis. This leads to inflammation & pain in these joints. Over time, this leads to excessive deposition of calcium & fusion of the joints. This makes the spine less flexible and can result in a hunched-forward posture. If joints that the ribs have with the spine are affected, it can make deep breathing difficult & painful.
Ankylosing Spondylitis tends to affect men more often than women. Signs and symptoms typically begin in early adulthood. It can also affect joints other than the spine like knee, ankle, shoulder. At times, the inflammation also can occur in other parts of your body especially the eyes.
Related Video

What is Ankylosing Spondylitis?
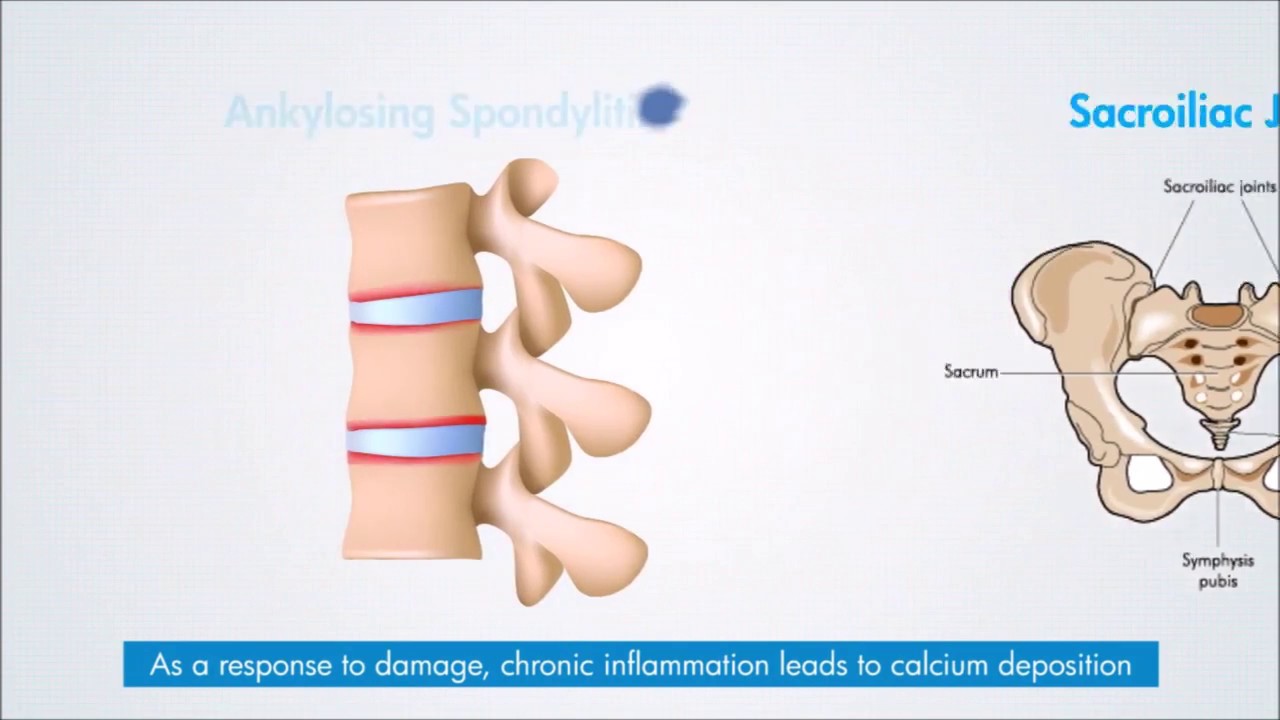
What is Ankylosing Spondylitis & how does it progress?

Ankylosing Spondylitis & axial SpondyloArthritis: what is the difference?
Early symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis include pain and stiffness in lower back, buttocks and hips. This pain is more in the night & increases with rest. The pain quite often awakens one from sleep particularly in the second half of sleep. One can also have stiffness in the back on getting up that takes 2-3 hours to settle. Neck pain and fatigue also are common. The pain may change locations & affects different parts of the back/ neck & may alternate from one buttock to the other.
The joints & areas most commonly affected are:
- The joint beneath the buttocks (buttock pain)
- The joints of the vertebrae (backache)
- The joints that the ribs have with the vertebrae (pain while taking deep breath)
- The places where tendons and ligaments attach to bones, mainly in the spine, but
- sometimes along the back of your heel & the heel itself (heel pain, pain behind the ankle)
- The cartilage between your breastbone and ribs (chest pain)
- Other joints including the hip, shoulder, ankles.
Related Video

Do you have Ankylosing Spondylitis?
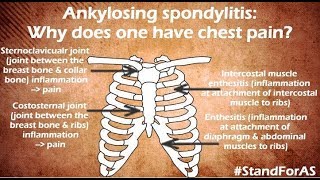
What is Ankylosing Spondylitis & how does it progress?

Various types of pelvic pain caused by Ankylosing Spondylitis

In AS, why is backache worse during the night or early morning?

Why is it painful to cough and sneeze when you have AS?
What causes foot ache in AS?
Ankylosing Spondylitis is an autoimmune condition & the exact cause of this autoimmunity is not known. Genetic factors seem to be involved & it tends to run in families. People who have a gene called HLA-B27 are at a greatly increased risk of developing Ankylosing Spondylitis. There are other genes too that are involved in the causation of Ankylosing Spondylitis. So, one can get Ankylosing Spondylitis without the HLA B27 gene being present. At the same time, every person with the HLA B27 gene need to develop Ankylosing Spondylitis. Only some people with the gene develop the condition.
Risk factors
- Sex - Men are more likely to develop Ankylosing Spondylitis than are women.
- Age — Onset generally occurs in late adolescence or early adulthood.
- Your heredity. Almost 80-90% of those who have Ankylosing Spondylitis have the HLA-B27 gene. However, many people who have this gene never develop Ankylosing Spondylitis.
- Smoking- smoking is linked to a more rapidly progressive Ankylosing Spondylitis. It has been linked with more fusion & progression.
Related Video

Does everyone with the HLA B27 gene have AS?

Does smoking affect Ankylosing Spondylitis?
In Ankylosing Spondylitis, over a period of time, calcium gets deposited & new bone forms as part of the body's attempt to heal. This bridges the gap between vertebrae and eventually fuses sections of vertebrae. Those parts of the spine become stiff and inflexible. Fusion can also affect the joints that ribs have with the vertebrae thus restricting deep breathing.
Uncontrolled inflammation of Ankylosing Spondylitis can damage the cartilage of the joints particularly the hip. This leads to osteoarthritis of the hip.
Related Video

Why does the hip pain with Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Other complications might include
Eye inflammation (uveitis) At times, the autoimmune process of Ankylosing Spondylitis tends to attack the eyes. This leads to uveitis & can cause eye pain, sensitivity to light and blurred vision.
Related Video

Uveitis: How does Ankylosing Spondylitis affect the eyes?

क्या Ankylosing Spondylitis आखों पर असर करता है? यूवैतिस (uveitis) क्या होता है?
Compression fractures Despite the excessive calcium deposition, the bones of the vertebrae are often weak. Weakened vertebrae can fracture. This can happen with minor jerks & at times with bending or lifting weights. This can cause sudden increase in the pain. Vertebral fractures can put pressure on and possibly injure the spinal cord and the nerves that pass through the spine.
Related Video

Sudden severe pain in the back with AS...what could be the reason?
Heart problems A 2015 review of studies did show that people living with AS had a significantly higher chance of developing coronary artery disease & heart attacks as compared to the general population. (Ungprasert P, Srivali N, Kittanamongkolchai W. Risk of coronary artery disease in patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Transl Med. 2015;3(4):51.) This is possibly due to the long term effect of the inflammation on the heart. Ankylosing Spondylitis can also cause inflammation aorta, the largest artery in the body. The inflamed aorta can distort the shape of the aortic valve in the heart, which impairs its function.
Pregnancy Ankylosing Spondylitis doesn't appear to affect fertility of one’s chances of getting pregnant. Majority of the women with Ankylosing Spondylitis are able to safely deliver a healthy baby. Some medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) — may not be safe to use during pregnancy. Backache, pelvic pain & the spinal fusion may pose a challenge during delivery. Proper planning & prior discussion with a rheumatologist can take care of these issues.
Related Video

How to plan pregnancy with Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Diagnosis
A rheumatologist suspects Ankylosing Spondylitis if one has inflammatory backache. Inflammatory backache would mean backache that is worse after rest & at night & that improves with activity. During the physical exam, mobility of the spine (neck, mid back & lower back) is checked. Pain on pressing the buttocks, flexing the thighs at the hip would be checked. Chest expansion would be looked at as Ankylosing Spondylitis restricts the same.
Related Video

How do we diagnose Ankylosing Spondylitis?
X-rays allow your doctor to check for changes in your sacroiliac joints & the joints of the vertebrae. However, Xray does not pick active inflammation but picks up the damage caused to the joints due to the inflammation & the calcification. Hence Xray picks up changes late in the course of Ankylosing Spondylitis.
An MRI shows active inflammation as well as damage to the joints. It can show inflammation in the sacroiliac joints, vertebral joints & the joints that ribs make with the vertebrae. MRI can pick up the inflammation early & help with an early diagnosis.
Related Video

What reports can confirm diagnosis of Ankylosing Spondylitis? Is it the Xray/ HLA B27/ MRI?
HLA B 27 test this is a blood test
HLA B27 is a gene that is strongly associated with Ankylosing Spondylitis. It is seen in almost 90% patients suffering from Ankylosing Spondylitis. However there are other genes that can cause Ankylosing Spondylitis as well & one can have AS without having the HLA B27 gene. HLA B27 gene is inherited from parents & having the gene does not necessarily mean that one would end up having Ankylosing Spondylitis.
ESR & CRP these tests indicate inflammatory process in the body & help assess the activity of Ankylosing Spondylitis. CRP is repeated on followup visits & helps keep a track of the AS activity.
Related Video

How do we diagnose Ankylosing Spondylitis?

What reports can confirm diagnosis of Ankylosing Spondylitis? Is it the Xray/ HLA B27/ MRI?

Is HLA B27 necessary for a diagnosis of Ankylosing Spondylitis?

क्या Ankylosing Spondylitis के लिए HLA B27 का पॉज़िटिव होना ज़रूरी है?
Treatment
There's no cure for Ankylosing Spondylitis, but treatment is available to control the arthritis & prevent progression as well as the complications. Treatment can help delay or prevent the process of the spine fusion and stiffening.
Ankylosing Spondylitis treatment is most successful early in the disease course before the disease causes irreversible damage to your joints.
Related Video

How to conquer Ankylosing Spondylitis? : A systematic practical plan.

Ankylosing Spondylitis को जीतने के १० नियम

Can we reverse vertebral fusion related to Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as naproxen (Naprosyn), indomethacin (Indocin, Indocid), etoricoxib (Retoz, etoshine) are the medications doctors most commonly use to treat Ankylosing Spondylitis. As the name suggests, they reduce the inflammation in the joints. Contrary to popular belief they are not just 'pain killers' but have a strong 'anti-inflammatory' function. The do reduce the inflammation associated with AS. They are used for prolonged period in AS to control the inflammation.
Related Video

Ankylosing Spondylitis treatment: Are NSAIDs useful?

What is the difference between traditional & COX-2 selective NSAIDs?
However, these medications can cause acidity, gastrointestinal bleeding, kidney issues. A rheumatologist would keep a watch on these possibilities during the treatment.
Related Video

NSAIDs (pain killers) for Ankylosing Spondylitis: 10 precautions to avoid side effects
Streoids Steroids are used as a short term treatment to manage a flare up of Ankylosing Spondylitis. But steroids have no long term use in treating Ankylosing Spondylitis.
Related Video

Ankylosing Spondylitis: क्या NSAIDs (दर्द शामक ) गोलियाँ लेकर AS अच्छा हो सकता है?

Ankylosing Spondylitis: कौनसा NSAID (दर्द शामक गोली) AS के लिए सबसे अच्छा है ?

10 सावधानिया NSAIDs (दर्द शामक गोलीया) की दुष्प्रभाव को रोकने के लिए
Sulphasalazine Sulphasalazine (Saaz, Sazo) is used by many rheumatologists for Ankylosing Spondylitis. Though there is no conclusive study about its effectiveness in reducing the backache of AS, it has been used traditionally. Many rheumatologist believe that it does help reduce the backache of AS.
Sulphasalazine & methotrexate are useful in reducing the inflammation of peripheral joints (knee, ankle, hand joints)
Related Video

Ankylosing Spondylitis: Know your medications: DMARDs

Ankylosing Spondylitis: कौनसी दवाई से अच्छा होता है? Sulphasalazine (साज/ साजों ) और अन्य DMARDs

क्या sulphasalzine (Saaz/ Sazo/ साज/ साजो) गोली पुरुषों में प्रजनन क्षमता को प्रभावित करती है?
If one’s backache persists despite NSAIDs & regular exercises, then biologics are thought of. Biologics include tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocker or an interleukin-17 (IL-17) inhibitor. TNF blockers target a chemical called TNF alpha that is produced in the body & responsible for inflammation associated with Ankylosing Spondylitis. IL-17 is another chemical produced in the body & is associated with inflammation of Ankylosing Spondylitis.
Related Video

What are biologics? How do they reduce inflammation in Ankylosing Spondylitis?
These chemicals (TNF alpha & IL-17 play a role in maintaining body’s immune defense & taking biologics that block these chemicals can increase one’s chances of infections. One is investigated thoroughly prior to staring a biologics to minimize the chances of infections later. In India, there is a particular concern about Tuberculosis. One is investigated for latent tuberculosis prior to starting biologics. One should take proper precautions while on biologics to reduce the possibility of catching an infection.
Related Video

Do Biologics cause Tuberculosis?

What precaution should one take to avoid infections while on biologics?
If one is unable to take TNF blockers or IL-17 inhibitors because of other health conditions, a rheumatologist may recommend the Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib (Xeljanz). This drug has been approved for psoriatic arthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Studies have shown its effectiveness in Ankylosing Spondylitis as well. Research is ongoing & its approval for Ankylosing Spondylitis is awaited.
Related Video

Tofacitinib: the promising new therapy for Ankylosing Spondylitis

Tofacitinib for Ankylosing Spondylitis- side effects & precautions

टोफ़ासितिनिब (Tofacitinib) गोली : आशा की नई किरण Ankylosing Spondylitis के लिए

टोफ़ासिटिनिब - जानिए एहतियात और साइड इफेक्ट्स के बारे में
Many patients feel that biologics are the only treatment options for Ankylosing Spondylitis. However, many patients suffering from Ankylosing Spondylitis, particularly in the early stage improve with NSAIDs & regular back exercises. Each & every person may not require a biologic therapy.
Related Video

Does every Ankylosing Spondylitis warrior require biologic therapy?
Ankylosing Spondylitis is an autoimmune ailment. One’s own immunity thinks that joints are foreign & attacks the joints causing inflammation. What if one can transplant this immunity just the way one does a transplant of the kidney, heart? This is the concept behind stem cell therapy. If the entire immune system that has started working against one’s own joints can be removed & replaced by a healthy immune system that would not attack the joints; Ankylosing Spondylitis can be cured. Stem cell therapy is being researched & not being used as a regular therapy currently for Ankylosing Spondylitis.
Related Video

What is stem cell therapy? Is it useful in Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Physical therapy is an integral part of treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Exercises can help reduce the pain, maintain flexibility of the spine & retard fusion.
Range-of-motion and stretching exercises can help maintain flexibility of the back & and preserve good posture. Proper sleeping and walking positions and back exercises can help prevent the hunch back posture.
Related Video

Stretches & exercises for Ankylosing Spondylitis
NSAIDs & regular exercises can induce remission in early Ankylosing Spondylitis. However, exercises alone may not be sufficient to control the arthritis & medications are also necessary.
Related Video

Can physiotherapy & exercise cure Ankylosing Spondylitis?
While exercising, one has to be careful not to put undue pressure on the spine. High impact exercises like jumping, skipping can put undue pressure on the spine & aggravate the backache.
Related Video

Exercises to be avoided in Ankylosing Spondylitis

Ankylosing Spondylitis में कौनसे व्यायाम नहीं करने चाहिए ?
Dr. Alan Ebringer proposed a theory that explained causation of AS & a possible dietary remedy. He proposed that klebsiella, a type of bacteria in one’s gut is responsible for AS. This bacteria feeds on starch & can be starved to death with a low starch diet. This lead to the ‘low starch or London AS diet”. Many AS patients do find relief in their symptoms with this diet. Dietary studies are difficult to conduct & the effectiveness of this dietary intervention has not been scientifically conclusively established.
Related Video

Low starch diet & Ankylosing Spondylitis: Part 1: scientific evidence

Low starch diet for Ankylosing Spondylitis | Part 2: All you need to know.

Ankylosing Spondylitis & low starch diet | Part 3: diet charts & plans

Low starch diet & Ankylosing Spondylitis | Part 4: What are the possible hazards? How to overcome?

क्या पेट और खानपान का एससे कोई सम्बंध है?

लो स्टार्च डाइयट का पालन कैसे कर सकते है ? दिनभर आहार कैसे ले?
Apart from the medicines & exercises, lifestyle changes do help relieve symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis. A good sleep can help reduce the pain & fatigue associated with Ankylosing Spondylitis.
A good mattress would help improve the quality of sleep.
Related Video

How to choose the right mattress for Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Sleeping posture can help maintain the correct posture & avoid the hunch back deformity in the long run. ‘Prone lying’ is one of the best sleeping postures for someone with Ankylosing Spondylitis. This helps keep the spine straight & reduces chances of hunchback deformity.
Related Video
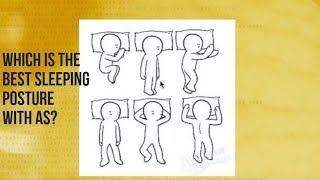
What is the best sleeping posture for Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Apart from pain, fatigue is also one of the common problem for one suffering from Ankylosing Spondylitis. This may be caused due to the inflammation of Ankylosing Spondylitis or fibromyalgia that often accompanies AS. Adequate control of AS, fibromyalgia & lifestyle changes can help one take care of the fatigue.
Related Video

How to conquer the fatigue of Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Success Stories

How can you conquer Ankylosing Spondylitis?

10 rules to conquer Ankylosing Spondylitis
Symptoms & Causes
Rheumatoid Arthritis is an autoimmune disease affecting the joints. Normally, body’s immune system is designed to fight organisms causing infections. Due to various reasons, the immune system may start considering its own body organs as foreign and attacks it. This self intolerance is known as autoimmunity. The condition it results into is called as autoimmune disease.
To understand the cause of joint swelling in Rheumatoid Arthritis, let us first understand the structure of a synovial joint. A joint is made up of two bones. It is lined on the inner side by a protective lining called the synovium.
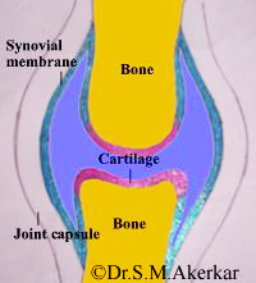
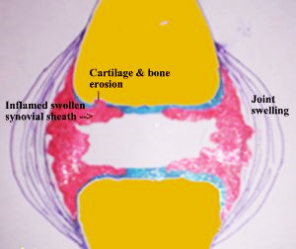
This synovium is the target of immune attack & gets swollen. To begin with the swelling is mild. Hence it is not very obvious from outside. HOwever, it does cause pain & stiffness of the joint. Later, as the swelling increases, it becomes clearly visible externally as well.l.
TThe swollen synovium in Rheumatoid Arthritis has destructive potential. If not treated, it begins damaging the underlying bones & cartilage. This damage involving the bones, cartilage and surrounding muscles leads to deformities.
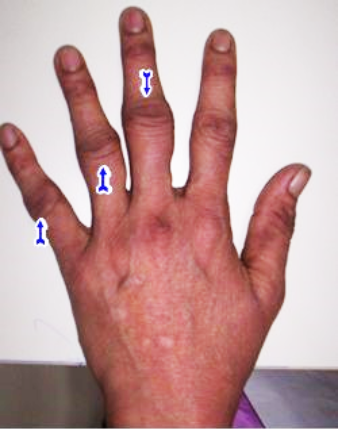
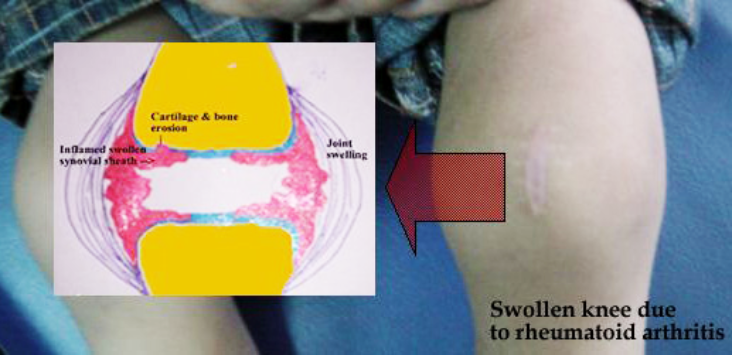
Rheumatoid Arthritis causes pain & swelling in multiple joints. It commonly affects the joints of the hands (knuckles and the first joint of the fingers) & feet. The wrist, elbow, shoulder, knee, and ankle can also be affected. Initially, a person may not experience obvious swelling in the said joints. However, there is pain & stiffness of these joints early in the morning. The stiffness settles after a hot water bath or as the joints are used. Later, as arthritis progresses, the swelling becomes obvious. One may also develop nodular swelling called rheumatoid nodules. These are commonly seen on the forearm below the elbow joint.

Rheumatoid Arthritis is an autoimmune condition & the exact cause of this autoimmunity is not known. Genetic factors seem to be involved & it tends to run in families. However one can suffer from Rheumatoid Arthritis without any family member suffering from it.
- Deformities - if not taken care of, Rheumatoid Arthritis can lead to disabling hand/ feet deformities in the long run. It is also important to note that if properly treated, deformities are uncommon.
- Osteoporosis- Rheumatoid Arthritis itself & steroids that are used to treat it can make the bones weak & fragile. This increase the risk of fractures.
- Eye complications- Rheumatoid Arthritis inflammation can affect the eyes causing scleritis/ episcleritis. Scleritis ((inflammation of the white part of the eye) is a serious condition & can cause vision loss.
- Lung complications- interstitial lung disease- Rheumatoid Arthritis can cause immune attack on the lung & consequent stiffening of the lungs.
Diagnosis
A rheumatologist suspects Rheumatoid Arthritis if one has multiple inflamed joints. Inflamed joints are characterized by pain & swelling. Rheumatologist will take your history & examine your joints. A diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis is based on the swelling in the joints & the pattern of the joints involved. There are other causes of inflamed joints as well & blood investigations, Xrays can help differentiate between them.
X-rays allow your doctor to check for changes in your joints. X rays of the joints do show characteristic changes & help confirm the diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. The characteristic changes include bone loss at the edges of the bone (erosions) & loss of joint cartilage (space).
X rays are often normal in early stages of Rheumatoid Arthritis & do not help much in diagnosing Rheumatoid Arthritis at an early stage.
Sonography/ MRI Sonography/ MRI can show the thickened synovium (joint lining) in the joints & confirm the diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sonography/ MRI help to diagnose Rheumatoid Arthritis early.
Rheumatoid factor this is a blood test This is a common investigation asked when Rheumatoid Arthritis is suspected. Rheumatoid factor is a protein produced by our immune system. High levels of rheumatoid factor are seen in Rheumatoid Arthritis. However, a few patients of Rheumatoid Arthritis may have normal levels of rheumatoid factor while some normal individuals may have high levels of rheumatoid factor. So, rheumatoid factor test is not diagnostic of Rheumatoid Arthritis & absence of rheumatoid factor does not always mean absence of Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Anti CCP antibody this is a blood test Anti CCP antibody stands for anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody. It is a protein produced by our immune system & is highly suggestive of Rheumatoid Arthritis. This is a very reliable test for Rheumatoid Arthritis & is better than rheumatoid factor in diagnosing Rheumatoid Arthritis (Diagnostic Accuracy of Anti–Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Antibody and Rheumatoid Factor for Rheumatoid Arthritis K. Nishimura, D. Sugiyama, Y. Kogata, G. Tsuji, T. Nakazawa, S. Kawano, K. Saigo, A. Morinobu, M. Koshiba, K. M. Kuntz, I. Kamae and S. Kumagai Ann Intern Med 2007; 797-808 ). High levels of the Anti CCP antibody does indicate a more aggressive RA & higher risk of joint damage as compared to a patient with low levels. (Kastbom, A., Strandberg, G., Lindroos, A. et al. 2004. Anti-CCP antibody test predicts the disease course during 3 years in early Rheumatoid Arthritis (the Swedish TIRA project). Ann. Rheum. Dis.,63:1085–9.) Anti CCP antibody may be negative in a few individuals with Rheumatoid Arthritis & a negative test does not rule out Rheumatoid Arthritis.
ESR & CRP these are blood test ESR/ CRP are blood tests to measure the inflammation in the body. Arthritis patients have high ESR & CRP due to the ongoing inflammation in the joints. However, arthritis is not the only condition associated with high ESR/ CRP. Infections, other autoimmune diseases will also lead to a high ESR/ CRP. It is best left to the doctor to interpret the ESR/ CRP result.
Treatment
Effective therapy is available for rheumatoid arthritis. DMARDs (Disease modifying anti rheumatic drugs) & if required biologics can control the inflammation of joints & prevent joint deformities. Rheumatoid arthritis is best treated early before it causes any damage to the joints.
NSAIDS stands for Non Steroidal Anti Inflammatory Drugs- NSAIDs reduce the inflammation & the pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis. NSAIDs are not used in the long run. They are used in the initial phases till the DMARDs control the arthritis activity & later during a flare.
DMARDs stands for Disease Modifying Anti Rheumatic Drugs These include- Methotrexate, Hydroxychloroquine, Sulphasalazine, Leflunomide These are the main medications for Rheumatoid Arthritis & are used in the long run to control the arthritis activity. They are effective agents & control the Rheumatoid Arthritis activity in the long run.
Biologics are genetically engineered proteins. They act on specific chemicals that control the inflammatory process.
Many biologics are available for Rheumatoid Arthritis. They include–
- TNF alpha blockers- Infliximab, Etanercept, Adalimumab, Golimumab, Sertolizumab
- IL-6 blockers- Tocilizumab
- B cell blocker- Rituximab
- T cell inhibitor- Abatacept
- IL-1 blocker- Anakinra
Related Video

What are biologics? How do they reduce inflammation in Ankylosing Spondylitis?
If Rheumatoid Arthritis remains active despite DMARDs, then biologics are thought of. Biologics do block chemicals involved in immune processes & can increase one’s chances of infections. One is investigated thoroughly prior to starting a biologics to minimize the chances of infections later. In India, there is a particular concern about Tuberculosis. One is investigated for latent tuberculosis prior to starting biologics. One should take proper precautions while on biologics to reduce the possibility of catching an infection.
Related Video

Do Biologics cause Tuberculosis?

What precaution should one take to avoid infections while on biologics?
Steroids or glucocorticoids reduce the inflammation in the joints. They are used during the initial 4-6 weeks of therapy & later during a flare. They are generally not used in the long run for controlling rheumatoid arthritis.
Physical therapy is an integral part of treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Exercises can help reduce the pain, maintain flexibility of the joints & prevent deformities.
Muscle weakness occurs in muscles around the inflamed joints due reduction in activities. Maintenance of normal muscle strength is important for physical & also for stabilization of the joints and prevention of falls.
Physiotherapy modalities-
- Heat/ cold application
- TENS electrostimulation
- Hydrotherapy
- Massage therapy
- Therapeutic exercise
Dietary interventions have shown substantial benefits in reducing disease symptoms such as pain, joint stiffness, swelling. One can benefit from avoiding foods that increase inflammation (anti inflammatory diet).
Symptoms & Causes
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by a buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. It generally starts as an episodic pain & swelling in the joints, particularly the joints of the great toe & feet. If not taken care of it can cause pain & swelling in other joints as well & has the potential to cause continuous pain in the joints. Over a period of time, if not taken care of it can lead to deformities of the joints & deposition of uric acid under the skin in the form of nodules called as tophi.
Gout can affect anyone. However men are more likely to be affected & get gout earlier than women. Women tend to get affected after menopause.
Gout causes epsiodes or attacks of pain & swelling in the joints. An episode can last 3-10 days. During an episode, the joint swells up & causes intense pain. In the majority, it starts with the joint of the great toe. In between the acute episodes, one does not have any joint pain. If these symptoms are neglected, gout can become chronic. It can then cause persistent pain & swelling in multiple joints.
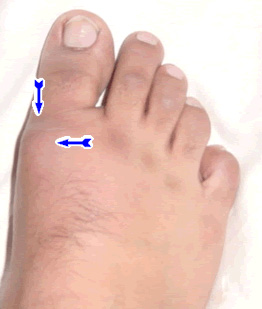
Uric acid can also get deposited under the skin. These nodules are called tophi. The white colour of the deposited uric acid is often seen under the nodules. They are generally painless but may get inflamed & may ulcerate leading to oozing of the white material (uric acid).
Our body makes a chemical called uric acid during breakdown of chemicals called purines. Purines are chemicals that are naturally created in our body & are also present in our food. Generally about 3/4th of the uric acid comes from the breakdown of purines in the body while 1/4th comes from the food. Generally the body gets rid of the uric acid in urine. However if the consumption of uric acid increases & the body is not able to get rid of uric acid then this leads to a buildup of uric acid in the blood. This in turn can then cause crystallization of the uric acid crystals in the joints leading to an episode of gout.
Risk factors
- Family history A person’s genes can increase the chances of gout. Genes do determine the kidney's handling of uric acid. If the kidney does not excrete uric acid adequately, a buildup of uric acid in the body can start.
- Obesity obesity increase the chances of gout. The more overweight one is, higher are the uric acid levels & higher the chances of gout.
- Gender & age Gout is more common in men than women. Women rarely get gout before menopause. Female hormone estrogen increases the uric acid excretion by the kidneys. Estrogen levels decrease after menopause & uric acid levels increase.
- High alcohol/ protein intake - Higher intake of alcohol/ protein increases the production of uric acid in the body. This may be more than what the kidney can handle & lead to gout.
- Medications: certain medications called diuretics can reduce the ability of the kidneys to take care of the uric acid & lead to increase in the blood uric acid levels.
If not adequately treated, chronic gout can cause deformities of the joints. The gouty tophi can at times compress nerves.
Diagnosis
A rheumatologist suspects gout if one has episodic pain & swelling of the joints. The suspicion is higher if joints of the feet are affected.
Xray An Xray of the feet/ swollen joint can show joint damage resulting from long standing gout.
Synovial fluid examination: Fluid is aspirated from the swollen joint & examined under a microscope. In case of gout, uric acid crystals can be seen under the microscope. This is a confirmatory test for gout.
Dual Energy CT (DECT): This is a special CT scan & can identify uric acid deposition in & around the joints. This is generally used in some cases to confirm the diagnosis of gout.
Uric acid level This is a blood test. A high uric acid level does suggest gout in the presence of/ history of episodic joint pain/ swelling. However uric acid level can be normal immedicately following an episode of gout.
Treatment
Effective therapy is available for Gout.
Treatment includes
- Treatment of the acute attack
- Long term treatment to prevent attacks
Treatment of the acute attack is aimed at pain relief & control of inflammation. This does not lower the blood uris acid level or prevent future attacks.
- NSAIDs used for pain relief & control of inflammation. If one has kidney failure due to gout/ other comorbidities, NSAIDs cannot be used
- Corticosteroids a short course is used for effective rapid control of inflammation. However, there is no role for long term corticosteroids.
- Colchicine this is not a pain killer but is very effective in reducing the uric acid related joint inflammation.
This is a long term treatment & aims to prevent future attacks by controlling the blood uric acid levels. These work either by reducing the uric acid production in the body or by increasing its excretion in the urine.
These are started after an acute attack has settled. Initially there is a higher risk of a gouty arthritis attack after the urate lowering therapy is started. Your doctor will generally continue NSAIDs/ colchicine for a few months after this therapy is started to take care of this risk.
- Allopurinol: This reduces the uric acid production in the body. One is started on a low dose & the dose is gradually adjusted over a period of time based on the blood uric acid levels. Allopurinol is broken down & excreted by the kidneys.
- Febuxostat: this reduces the uric acid production in the body. One is started on a low dose & the dose is gradually adjusted over a period of time based on the blood uric acid levels. This is broken down by the liver & is preferred over allopurinol if one ha s a kidney failure.
- Probenecid: This increases the uric acid excretion. This is not widely available & hence not commonly used.
Diet is extremely important in prevention of gout attacks. Many food items can increase the blood uric acid levels & trigger an attack.
- Alcohol- gets converted into uric acid in the body. Beer is particularly important as it can lead to high uric acid levels. Wine consumption does not lead to an increase in the uric acid levels.
- Water intake: Water helps kidneys flush uric acid in the urine. One should drink at least 2 litres of water daily.
- Sweetened soft drinks: these contain high fructose corn syrup. This gets converted to uric acid in the body & should be avoided
- Vegetables & low fat/ no fat dairy products are recommended
- Meat & seafood are a major culprit & their consumption needs to be moderated.
Symptoms & Causes
Ankylosing Spondylitis is an autoimmune inflammatory disease. The immune system attacks the joints of the spine & pelvis. This leads to inflammation & pain in these joints. Over time, this leads to excessive deposition of calcium & fusion of the joints. This makes the spine less flexible and can result in a hunched-forward posture. If joints that the ribs have with the spine are affected, it can make deep breathing difficult & painful.
Ankylosing Spondylitis tends to affect men more often than women. Signs and symptoms typically begin in early adulthood. It can also affect joints other than the spine like knee, ankle, shoulder. At times, the inflammation also can occur in other parts of your body especially the eyes.
Related Video

What is Ankylosing Spondylitis?

What is Ankylosing Spondylitis & how does it progress?

Ankylosing Spondylitis & axial SpondyloArthritis: what is the difference?
Early symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis include pain and stiffness in lower back, buttocks and hips. This pain is more in the night & increases with rest. The pain quite often awakens one from sleep particularly in the second half of sleep. One can also have stiffness in the back on getting up that takes 2-3 hours to settle. Neck pain and fatigue also are common. The pain may change locations & affects different parts of the back/ neck & may alternate from one buttock to the other.
The joints & areas most commonly affected are:
- The joint beneath the buttocks (buttock pain)
- The joints of the vertebrae (backache)
- The joints that the ribs have with the vertebrae (pain while taking deep breath)
- The places where tendons and ligaments attach to bones, mainly in the spine, but
- sometimes along the back of your heel & the heel itself (heel pain, pain behind the ankle)
- The cartilage between your breastbone and ribs (chest pain)
- Other joints including the hip, shoulder, ankles.
Related Video

Do you have Ankylosing Spondylitis?

What is Ankylosing Spondylitis & how does it progress?

Various types of pelvic pain caused by Ankylosing Spondylitis

In AS, why is backache worse during the night or early morning?

Why is it painful to cough and sneeze when you have AS?

What causes foot ache in AS?
Ankylosing Spondylitis is an autoimmune condition & the exact cause of this autoimmunity is not known. Genetic factors seem to be involved & it tends to run in families. People who have a gene called HLA-B27 are at a greatly increased risk of developing Ankylosing Spondylitis. There are other genes too that are involved in the causation of Ankylosing Spondylitis. So, one can get Ankylosing Spondylitis without the HLA B27 gene being present. At the same time, every person with the HLA B27 gene need to develop Ankylosing Spondylitis. Only some people with the gene develop the condition.
Risk factors
- Sex - Men are more likely to develop Ankylosing Spondylitis than are women.
- Age — Onset generally occurs in late adolescence or early adulthood.
- Your heredity. Almost 80-90% of those who have Ankylosing Spondylitis have the HLA-B27 gene. However, many people who have this gene never develop Ankylosing Spondylitis.
- Smoking- smoking is linked to a more rapidly progressive Ankylosing Spondylitis. It has been linked with more fusion & progression.
Related Video

Does everyone with the HLA B27 gene have AS?

Does smoking affect Ankylosing Spondylitis?
In Ankylosing Spondylitis, over a period of time, calcium gets deposited & new bone forms as part of the body's attempt to heal. This bridges the gap between vertebrae and eventually fuses sections of vertebrae. Those parts of the spine become stiff and inflexible. Fusion can also affect the joints that ribs have with the vertebrae thus restricting deep breathing.
Uncontrolled inflammation of Ankylosing Spondylitis can damage the cartilage of the joints particularly the hip. This leads to osteoarthritis of the hip.
Related Video

Why does the hip pain with Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Other complications might include
Eye inflammation (uveitis) At times, the autoimmune process of Ankylosing Spondylitis tends to attack the eyes. This leads to uveitis & can cause eye pain, sensitivity to light and blurred vision.
Related Video

Uveitis: How does Ankylosing Spondylitis affect the eyes?

क्या Ankylosing Spondylitis आखों पर असर करता है? यूवैतिस (uveitis) क्या होता है?
Compression fractures Despite the excessive calcium deposition, the bones of the vertebrae are often weak. Weakened vertebrae can fracture. This can happen with minor jerks & at times with bending or lifting weights. This can cause sudden increase in the pain. Vertebral fractures can put pressure on and possibly injure the spinal cord and the nerves that pass through the spine.
Related Video

Sudden severe pain in the back with AS...what could be the reason?
Heart problems A 2015 review of studies did show that people living with AS had a significantly higher chance of developing coronary artery disease & heart attacks as compared to the general population. (Ungprasert P, Srivali N, Kittanamongkolchai W. Risk of coronary artery disease in patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Transl Med. 2015;3(4):51.) This is possibly due to the long term effect of the inflammation on the heart. Ankylosing Spondylitis can also cause inflammation aorta, the largest artery in the body. The inflamed aorta can distort the shape of the aortic valve in the heart, which impairs its function.
Pregnancy Ankylosing Spondylitis doesn't appear to affect fertility of one’s chances of getting pregnant. Majority of the women with Ankylosing Spondylitis are able to safely deliver a healthy baby. Some medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) — may not be safe to use during pregnancy. Backache, pelvic pain & the spinal fusion may pose a challenge during delivery. Proper planning & prior discussion with a rheumatologist can take care of these issues.
Related Video

How to plan pregnancy with Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Diagnosis
A rheumatologist suspects Ankylosing Spondylitis if one has inflammatory backache. Inflammatory backache would mean backache that is worse after rest & at night & that improves with activity. During the physical exam, mobility of the spine (neck, mid back & lower back) is checked. Pain on pressing the buttocks, flexing the thighs at the hip would be checked. Chest expansion would be looked at as Ankylosing Spondylitis restricts the same.
Related Video

How do we diagnose Ankylosing Spondylitis?
X-rays allow your doctor to check for changes in your sacroiliac joints & the joints of the vertebrae. However, Xray does not pick active inflammation but picks up the damage caused to the joints due to the inflammation & the calcification. Hence Xray picks up changes late in the course of Ankylosing Spondylitis.
An MRI shows active inflammation as well as damage to the joints. It can show inflammation in the sacroiliac joints, vertebral joints & the joints that ribs make with the vertebrae. MRI can pick up the inflammation early & help with an early diagnosis.
Related Video

What reports can confirm diagnosis of Ankylosing Spondylitis? Is it the Xray/ HLA B27/ MRI?
HLA B 27 test this is a blood test
HLA B27 is a gene that is strongly associated with Ankylosing Spondylitis. It is seen in almost 90% patients suffering from Ankylosing Spondylitis. However there are other genes that can cause Ankylosing Spondylitis as well & one can have AS without having the HLA B27 gene. HLA B27 gene is inherited from parents & having the gene does not necessarily mean that one would end up having Ankylosing Spondylitis.
ESR & CRP these tests indicate inflammatory process in the body & help assess the activity of Ankylosing Spondylitis. CRP is repeated on followup visits & helps keep a track of the AS activity.
Related Video

How do we diagnose Ankylosing Spondylitis?

What reports can confirm diagnosis of Ankylosing Spondylitis? Is it the Xray/ HLA B27/ MRI?

Is HLA B27 necessary for a diagnosis of Ankylosing Spondylitis?

क्या Ankylosing Spondylitis के लिए HLA B27 का पॉज़िटिव होना ज़रूरी है?
Treatment
There's no cure for Ankylosing Spondylitis, but treatment is available to control the arthritis & prevent progression as well as the complications. Treatment can help delay or prevent the process of the spine fusion and stiffening.
Ankylosing Spondylitis treatment is most successful early in the disease course before the disease causes irreversible damage to your joints.
Related Video

How to conquer Ankylosing Spondylitis? : A systematic practical plan.

Ankylosing Spondylitis को जीतने के १० नियम

Can we reverse vertebral fusion related to Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as naproxen (Naprosyn), indomethacin (Indocin, Indocid), etoricoxib (Retoz, etoshine) are the medications doctors most commonly use to treat Ankylosing Spondylitis. As the name suggests, they reduce the inflammation in the joints. Contrary to popular belief they are not just 'pain killers' but have a strong 'anti-inflammatory' function. The do reduce the inflammation associated with AS. They are used for prolonged period in AS to control the inflammation.
Related Video

Ankylosing Spondylitis treatment: Are NSAIDs useful?

What is the difference between traditional & COX-2 selective NSAIDs?
However, these medications can cause acidity, gastrointestinal bleeding, kidney issues. A rheumatologist would keep a watch on these possibilities during the treatment.
Related Video

NSAIDs (pain killers) for Ankylosing Spondylitis: 10 precautions to avoid side effects
Streoids Steroids are used as a short term treatment to manage a flare up of Ankylosing Spondylitis. But steroids have no long term use in treating Ankylosing Spondylitis.
Related Video

Ankylosing Spondylitis: क्या NSAIDs (दर्द शामक ) गोलियाँ लेकर AS अच्छा हो सकता है?

Ankylosing Spondylitis: कौनसा NSAID (दर्द शामक गोली) AS के लिए सबसे अच्छा है ?

10 सावधानिया NSAIDs (दर्द शामक गोलीया) की दुष्प्रभाव को रोकने के लिए
Sulphasalazine Sulphasalazine (Saaz, Sazo) is used by many rheumatologists for Ankylosing Spondylitis. Though there is no conclusive study about its effectiveness in reducing the backache of AS, it has been used traditionally. Many rheumatologist believe that it does help reduce the backache of AS.
Sulphasalazine & methotrexate are useful in reducing the inflammation of peripheral joints (knee, ankle, hand joints)
Related Video

Ankylosing Spondylitis: Know your medications: DMARDs

Ankylosing Spondylitis: कौनसी दवाई से अच्छा होता है? Sulphasalazine (साज/ साजों ) और अन्य DMARDs

क्या sulphasalzine (Saaz/ Sazo/ साज/ साजो) गोली पुरुषों में प्रजनन क्षमता को प्रभावित करती है?
If one’s backache persists despite NSAIDs & regular exercises, then biologics are thought of. Biologics include tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocker or an interleukin-17 (IL-17) inhibitor. TNF blockers target a chemical called TNF alpha that is produced in the body & responsible for inflammation associated with Ankylosing Spondylitis. IL-17 is another chemical produced in the body & is associated with inflammation of Ankylosing Spondylitis.
Related Video

What are biologics? How do they reduce inflammation in Ankylosing Spondylitis?
These chemicals (TNF alpha & IL-17 play a role in maintaining body’s immune defense & taking biologics that block these chemicals can increase one’s chances of infections. One is investigated thoroughly prior to staring a biologics to minimize the chances of infections later. In India, there is a particular concern about Tuberculosis. One is investigated for latent tuberculosis prior to starting biologics. One should take proper precautions while on biologics to reduce the possibility of catching an infection.
Related Video

Do Biologics cause Tuberculosis?

What precaution should one take to avoid infections while on biologics?
If one is unable to take TNF blockers or IL-17 inhibitors because of other health conditions, a rheumatologist may recommend the Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib (Xeljanz). This drug has been approved for psoriatic arthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Studies have shown its effectiveness in Ankylosing Spondylitis as well. Research is ongoing & its approval for Ankylosing Spondylitis is awaited.
Related Video

Tofacitinib: the promising new therapy for Ankylosing Spondylitis

Tofacitinib for Ankylosing Spondylitis- side effects & precautions

टोफ़ासितिनिब (Tofacitinib) गोली : आशा की नई किरण Ankylosing Spondylitis के लिए

टोफ़ासिटिनिब - जानिए एहतियात और साइड इफेक्ट्स के बारे में
Many patients feel that biologics are the only treatment options for Ankylosing Spondylitis. However, many patients suffering from Ankylosing Spondylitis, particularly in the early stage improve with NSAIDs & regular back exercises. Each & every person may not require a biologic therapy.
Related Video

Does every Ankylosing Spondylitis warrior require biologic therapy?
Ankylosing Spondylitis is an autoimmune ailment. One’s own immunity thinks that joints are foreign & attacks the joints causing inflammation. What if one can transplant this immunity just the way one does a transplant of the kidney, heart? This is the concept behind stem cell therapy. If the entire immune system that has started working against one’s own joints can be removed & replaced by a healthy immune system that would not attack the joints; Ankylosing Spondylitis can be cured. Stem cell therapy is being researched & not being used as a regular therapy currently for Ankylosing Spondylitis.
Related Video

What is stem cell therapy? Is it useful in Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Physical therapy is an integral part of treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Exercises can help reduce the pain, maintain flexibility of the spine & retard fusion.
Range-of-motion and stretching exercises can help maintain flexibility of the back & and preserve good posture. Proper sleeping and walking positions and back exercises can help prevent the hunch back posture.
Related Video

Stretches & exercises for Ankylosing Spondylitis
NSAIDs & regular exercises can induce remission in early Ankylosing Spondylitis. However, exercises alone may not be sufficient to control the arthritis & medications are also necessary.
Related Video

Can physiotherapy & exercise cure Ankylosing Spondylitis?
While exercising, one has to be careful not to put undue pressure on the spine. High impact exercises like jumping, skipping can put undue pressure on the spine & aggravate the backache.
Related Video

Exercises to be avoided in Ankylosing Spondylitis

Ankylosing Spondylitis में कौनसे व्यायाम नहीं करने चाहिए ?
Dr. Alan Ebringer proposed a theory that explained causation of AS & a possible dietary remedy. He proposed that klebsiella, a type of bacteria in one’s gut is responsible for AS. This bacteria feeds on starch & can be starved to death with a low starch diet. This lead to the ‘low starch or London AS diet”. Many AS patients do find relief in their symptoms with this diet. Dietary studies are difficult to conduct & the effectiveness of this dietary intervention has not been scientifically conclusively established.
Related Video

Low starch diet & Ankylosing Spondylitis: Part 1: scientific evidence

Low starch diet for Ankylosing Spondylitis | Part 2: All you need to know.

Ankylosing Spondylitis & low starch diet | Part 3: diet charts & plans

Low starch diet & Ankylosing Spondylitis | Part 4: What are the possible hazards? How to overcome?

क्या पेट और खानपान का एससे कोई सम्बंध है?

लो स्टार्च डाइयट का पालन कैसे कर सकते है ? दिनभर आहार कैसे ले?
Apart from the medicines & exercises, lifestyle changes do help relieve symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis. A good sleep can help reduce the pain & fatigue associated with Ankylosing Spondylitis.
A good mattress would help improve the quality of sleep.
Related Video

How to choose the right mattress for Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Sleeping posture can help maintain the correct posture & avoid the hunch back deformity in the long run. ‘Prone lying’ is one of the best sleeping postures for someone with Ankylosing Spondylitis. This helps keep the spine straight & reduces chances of hunchback deformity.
Related Video

What is the best sleeping posture for Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Apart from pain, fatigue is also one of the common problem for one suffering from Ankylosing Spondylitis. This may be caused due to the inflammation of Ankylosing Spondylitis or fibromyalgia that often accompanies AS. Adequate control of AS, fibromyalgia & lifestyle changes can help one take care of the fatigue.
Related Video

How to conquer the fatigue of Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Success Stories

How can you conquer Ankylosing Spondylitis?

10 rules to conquer Ankylosing Spondylitis
Symptoms & Causes
Rheumatoid Arthritis is an autoimmune disease affecting the joints. Normally, body’s immune system is designed to fight organisms causing infections. Due to various reasons, the immune system may start considering its own body organs as foreign and attacks it. This self intolerance is known as autoimmunity. The condition it results into is called as autoimmune disease.
To understand the cause of joint swelling in Rheumatoid Arthritis, let us first understand the structure of a synovial joint. A joint is made up of two bones. It is lined on the inner side by a protective lining called the synovium.

This synovium is the target of immune attack & gets swollen. To begin with the swelling is mild. Hence it is not very obvious from outside. HOwever, it does cause pain & stiffness of the joint. Later, as the swelling increases, it becomes clearly visible externally as well.l.
TThe swollen synovium in Rheumatoid Arthritis has destructive potential. If not treated, it begins damaging the underlying bones & cartilage. This damage involving the bones, cartilage and surrounding muscles leads to deformities.

Rheumatoid Arthritis causes pain & swelling in multiple joints. It commonly affects the joints of the hands (knuckles and the first joint of the fingers) & feet. The wrist, elbow, shoulder, knee, and ankle can also be affected. Initially, a person may not experience obvious swelling in the said joints. However, there is pain & stiffness of these joints early in the morning. The stiffness settles after a hot water bath or as the joints are used. Later, as arthritis progresses, the swelling becomes obvious. One may also develop nodular swelling called rheumatoid nodules. These are commonly seen on the forearm below the elbow joint.



Rheumatoid Arthritis is an autoimmune condition & the exact cause of this autoimmunity is not known. Genetic factors seem to be involved & it tends to run in families. However one can suffer from Rheumatoid Arthritis without any family member suffering from it.
- Deformities - if not taken care of, Rheumatoid Arthritis can lead to disabling hand/ feet deformities in the long run. It is also important to note that if properly treated, deformities are uncommon.
- Osteoporosis- Rheumatoid Arthritis itself & steroids that are used to treat it can make the bones weak & fragile. This increase the risk of fractures.
- Eye complications- Rheumatoid Arthritis inflammation can affect the eyes causing scleritis/ episcleritis. Scleritis ((inflammation of the white part of the eye) is a serious condition & can cause vision loss.
- Lung complications- interstitial lung disease- Rheumatoid Arthritis can cause immune attack on the lung & consequent stiffening of the lungs.
Diagnosis
A rheumatologist suspects Rheumatoid Arthritis if one has multiple inflamed joints. Inflamed joints are characterized by pain & swelling. Rheumatologist will take your history & examine your joints. A diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis is based on the swelling in the joints & the pattern of the joints involved. There are other causes of inflamed joints as well & blood investigations, Xrays can help differentiate between them.
X-rays allow your doctor to check for changes in your joints. X rays of the joints do show characteristic changes & help confirm the diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. The characteristic changes include bone loss at the edges of the bone (erosions) & loss of joint cartilage (space).
X rays are often normal in early stages of Rheumatoid Arthritis & do not help much in diagnosing Rheumatoid Arthritis at an early stage.
Sonography/ MRI Sonography/ MRI can show the thickened synovium (joint lining) in the joints & confirm the diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sonography/ MRI help to diagnose Rheumatoid Arthritis early.
Rheumatoid factor this is a blood test This is a common investigation asked when Rheumatoid Arthritis is suspected. Rheumatoid factor is a protein produced by our immune system. High levels of rheumatoid factor are seen in Rheumatoid Arthritis. However, a few patients of Rheumatoid Arthritis may have normal levels of rheumatoid factor while some normal individuals may have high levels of rheumatoid factor. So, rheumatoid factor test is not diagnostic of Rheumatoid Arthritis & absence of rheumatoid factor does not always mean absence of Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Anti CCP antibody this is a blood test Anti CCP antibody stands for anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody. It is a protein produced by our immune system & is highly suggestive of Rheumatoid Arthritis. This is a very reliable test for Rheumatoid Arthritis & is better than rheumatoid factor in diagnosing Rheumatoid Arthritis (Diagnostic Accuracy of Anti–Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Antibody and Rheumatoid Factor for Rheumatoid Arthritis K. Nishimura, D. Sugiyama, Y. Kogata, G. Tsuji, T. Nakazawa, S. Kawano, K. Saigo, A. Morinobu, M. Koshiba, K. M. Kuntz, I. Kamae and S. Kumagai Ann Intern Med 2007; 797-808 ). High levels of the Anti CCP antibody does indicate a more aggressive RA & higher risk of joint damage as compared to a patient with low levels. (Kastbom, A., Strandberg, G., Lindroos, A. et al. 2004. Anti-CCP antibody test predicts the disease course during 3 years in early Rheumatoid Arthritis (the Swedish TIRA project). Ann. Rheum. Dis.,63:1085–9.) Anti CCP antibody may be negative in a few individuals with Rheumatoid Arthritis & a negative test does not rule out Rheumatoid Arthritis.
ESR & CRP these are blood test ESR/ CRP are blood tests to measure the inflammation in the body. Arthritis patients have high ESR & CRP due to the ongoing inflammation in the joints. However, arthritis is not the only condition associated with high ESR/ CRP. Infections, other autoimmune diseases will also lead to a high ESR/ CRP. It is best left to the doctor to interpret the ESR/ CRP result.
Treatment
There's no cure for Ankylosing Spondylitis, but treatment is available to control the arthritis & prevent progression as well as the complications. Treatment can help delay or prevent the process of the spine fusion and stiffening.
Ankylosing Spondylitis treatment is most successful early in the disease course before the disease causes irreversible damage to your joints.
Effective therapy is available for rheumatoid arthritis. DMARDs (Disease modifying anti rheumatic drugs) & if required biologics can control the inflammation of joints & prevent joint deformities. Rheumatoid arthritis is best treated early before it causes any damage to the joints.
NSAIDS stands for Non Steroidal Anti Inflammatory Drugs- NSAIDs reduce the inflammation & the pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis. NSAIDs are not used in the long run. They are used in the initial phases till the DMARDs control the arthritis activity & later during a flare.
DMARDs stands for Disease Modifying Anti Rheumatic Drugs These include- Methotrexate, Hydroxychloroquine, Sulphasalazine, Leflunomide These are the main medications for Rheumatoid Arthritis & are used in the long run to control the arthritis activity. They are effective agents & control the Rheumatoid Arthritis activity in the long run.
Biologics are genetically engineered proteins. They act on specific chemicals that control the inflammatory process.
Many biologics are available for Rheumatoid Arthritis. They include–
- TNF alpha blockers- Infliximab, Etanercept, Adalimumab, Golimumab, Sertolizumab
- IL-6 blockers- Tocilizumab
- B cell blocker- Rituximab
- T cell inhibitor- Abatacept
- IL-1 blocker- Anakinra
Related Video

What are biologics? How do they reduce inflammation in Ankylosing Spondylitis?
If Rheumatoid Arthritis remains active despite DMARDs, then biologics are thought of. Biologics do block chemicals involved in immune processes & can increase one’s chances of infections. One is investigated thoroughly prior to starting a biologics to minimize the chances of infections later. In India, there is a particular concern about Tuberculosis. One is investigated for latent tuberculosis prior to starting biologics. One should take proper precautions while on biologics to reduce the possibility of catching an infection.
Related Video

Do Biologics cause Tuberculosis?

What precaution should one take to avoid infections while on biologics?
Steroids or glucocorticoids reduce the inflammation in the joints. They are used during the initial 4-6 weeks of therapy & later during a flare. They are generally not used in the long run for controlling rheumatoid arthritis.
Physical therapy is an integral part of treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Exercises can help reduce the pain, maintain flexibility of the joints & prevent deformities.
Muscle weakness occurs in muscles around the inflamed joints due reduction in activities. Maintenance of normal muscle strength is important for physical & also for stabilization of the joints and prevention of falls.
Physiotherapy modalities-
- Heat/ cold application
- TENS electrostimulation
- Hydrotherapy
- Massage therapy
- Therapeutic exercise
Dietary interventions have shown substantial benefits in reducing disease symptoms such as pain, joint stiffness, swelling. One can benefit from avoiding foods that increase inflammation (anti inflammatory diet).
Symptoms & Causes
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by a buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. It generally starts as an episodic pain & swelling in the joints, particularly the joints of the great toe & feet. If not taken care of it can cause pain & swelling in other joints as well & has the potential to cause continuous pain in the joints. Over a period of time, if not taken care of it can lead to deformities of the joints & deposition of uric acid under the skin in the form of nodules called as tophi.
Gout can affect anyone. However men are more likely to be affected & get gout earlier than women. Women tend to get affected after menopause.
Gout causes epsiodes or attacks of pain & swelling in the joints. An episode can last 3-10 days. During an episode, the joint swells up & causes intense pain. In the majority, it starts with the joint of the great toe. In between the acute episodes, one does not have any joint pain. If these symptoms are neglected, gout can become chronic. It can then cause persistent pain & swelling in multiple joints.

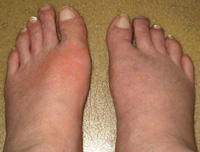
Uric acid can also get deposited under the skin. These nodules are called tophi. The white colour of the deposited uric acid is often seen under the nodules. They are generally painless but may get inflamed & may ulcerate leading to oozing of the white material (uric acid).

Our body makes a chemical called uric acid during breakdown of chemicals called purines. Purines are chemicals that are naturally created in our body & are also present in our food. Generally about 3/4th of the uric acid comes from the breakdown of purines in the body while 1/4th comes from the food. Generally the body gets rid of the uric acid in urine. However if the consumption of uric acid increases & the body is not able to get rid of uric acid then this leads to a buildup of uric acid in the blood. This in turn can then cause crystallization of the uric acid crystals in the joints leading to an episode of gout.
Risk factors
- Family history A person’s genes can increase the chances of gout. Genes do determine the kidney's handling of uric acid. If the kidney does not excrete uric acid adequately, a buildup of uric acid in the body can start.
- Obesity obesity increase the chances of gout. The more overweight one is, higher are the uric acid levels & higher the chances of gout.
- Gender & age Gout is more common in men than women. Women rarely get gout before menopause. Female hormone estrogen increases the uric acid excretion by the kidneys. Estrogen levels decrease after menopause & uric acid levels increase.
- High alcohol/ protein intake - Higher intake of alcohol/ protein increases the production of uric acid in the body. This may be more than what the kidney can handle & lead to gout.
- Medications: certain medications called diuretics can reduce the ability of the kidneys to take care of the uric acid & lead to increase in the blood uric acid levels.
If not adequately treated, chronic gout can cause deformities of the joints. The gouty tophi can at times compress nerves.
Diagnosis
A rheumatologist suspects gout if one has episodic pain & swelling of the joints. The suspicion is higher if joints of the feet are affected.
Xray An Xray of the feet/ swollen joint can show joint damage resulting from long standing gout.
Synovial fluid examination: Fluid is aspirated from the swollen joint & examined under a microscope. In case of gout, uric acid crystals can be seen under the microscope. This is a confirmatory test for gout.
Dual Energy CT (DECT): This is a special CT scan & can identify uric acid deposition in & around the joints. This is generally used in some cases to confirm the diagnosis of gout.
Uric acid level This is a blood test. A high uric acid level does suggest gout in the presence of/ history of episodic joint pain/ swelling. However uric acid level can be normal immedicately following an episode of gout.
Treatment
Effective therapy is available for Gout.
Treatment includes
- Treatment of the acute attack
- Long term treatment to prevent attacks
Treatment of the acute attack is aimed at pain relief & control of inflammation. This does not lower the blood uris acid level or prevent future attacks.
- NSAIDs used for pain relief & control of inflammation. If one has kidney failure due to gout/ other comorbidities, NSAIDs cannot be used
- Corticosteroids a short course is used for effective rapid control of inflammation. However, there is no role for long term corticosteroids.
- Colchicine this is not a pain killer but is very effective in reducing the uric acid related joint inflammation.
This is a long term treatment & aims to prevent future attacks by controlling the blood uric acid levels. These work either by reducing the uric acid production in the body or by increasing its excretion in the urine.
These are started after an acute attack has settled. Initially there is a higher risk of a gouty arthritis attack after the urate lowering therapy is started. Your doctor will generally continue NSAIDs/ colchicine for a few months after this therapy is started to take care of this risk.
- Allopurinol: This reduces the uric acid production in the body. One is started on a low dose & the dose is gradually adjusted over a period of time based on the blood uric acid levels. Allopurinol is broken down & excreted by the kidneys.
- Febuxostat: this reduces the uric acid production in the body. One is started on a low dose & the dose is gradually adjusted over a period of time based on the blood uric acid levels. This is broken down by the liver & is preferred over allopurinol if one ha s a kidney failure.
- Probenecid: This increases the uric acid excretion. This is not widely available & hence not commonly used.
Diet is extremely important in prevention of gout attacks. Many food items can increase the blood uric acid levels & trigger an attack.
- Alcohol- gets converted into uric acid in the body. Beer is particularly important as it can lead to high uric acid levels. Wine consumption does not lead to an increase in the uric acid levels.
- Water intake: Water helps kidneys flush uric acid in the urine. One should drink at least 2 litres of water daily.
- Sweetened soft drinks: these contain high fructose corn syrup. This gets converted to uric acid in the body & should be avoided
- Vegetables & low fat/ no fat dairy products are recommended
- Meat & seafood are a major culprit & their consumption needs to be moderated.
